You can use the WAN Replication menu item to check the status of WAN replication, synchronize map and cache data structures across clusters, and add dynamic configuration for WAN replication.
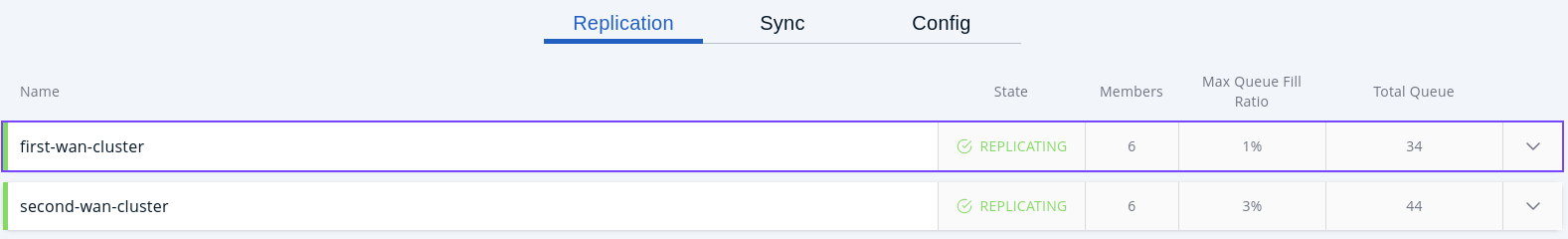
On this page, you see the WAN Replication Configurations that contain replication publishers.
-
Name: Name of the WAN replication config.
-
State: Current state of the WAN replication or publisher. See Changing WAN Publisher State for the list of possible WAN publisher states.
-
Members: Count of WAN publishers on the cluster members.
Members = (Cluster Members) * (WAN publishers).
-
Max Queue Fill Ratio: Maximum value of Outbound Queue Fill Ratio among the publishers.
-
Total Queue: Sum of Outbound Queue Size from the publishers.
To see the replication publishers, click on a replication config.
For detailed information about the corresponding replication publisher, click Show details.
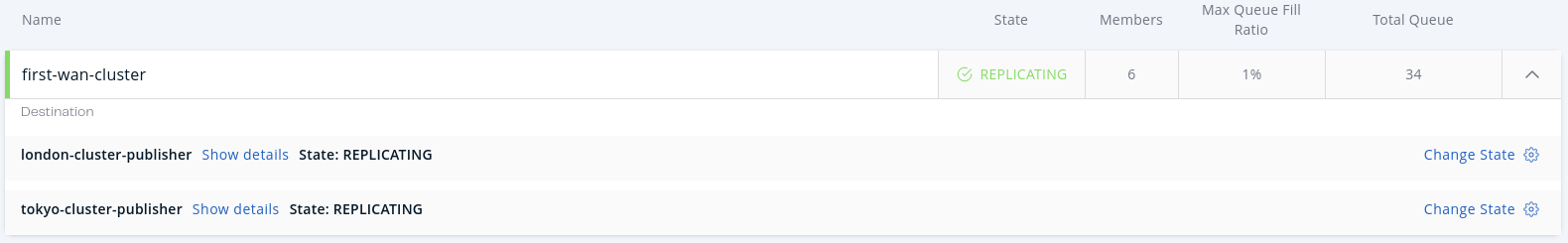
This page includes the following details:
-
Member: Hazelcast cluster member that has a WAN publisher. Icon shows the connection state (red=disconnected/green=connected).
-
Action: Pause, stop or resume replication of a member’s records. You can also clear the event queues in a member using the Clear Queues action. For example, if you know that the target cluster is being shut down, decommissioned, or put out of use and it will never come back, you may additionally clear the WAN queues to release the consumed heap after the publisher has been switched. Or, when a failure happens and queues are not replicated anymore, you could manually clear the queues using the Clear Queues action.
-
State: Shows current state of the WAN publisher on a member. See Changing WAN Publisher State for the list of possible WAN publisher states.
-
Events Published per Second: Number of published events per second. Please see the paragraph below.
-
Average Event Latency: Average latency of sending a record to the target from this member. See below for details.
-
Outbound Queue Fill Ratio: Percentage of how full the outbound queue is.
Outbound Queue Fill Ratio = (Outbound Queue Size / Outbound Queue Capacity) * 100 -
Outbound Queue Size: Number of records waiting in the queue to be sent to the target.
Events Published per Second and Average Event Latency are based on the following internal statistics:
-
Total published event count (TBEC): Total number of events that are successfully sent to the target cluster since the start-up of the member.
-
Total latency (TL): Grand total of each event’s waiting time in the queue, including network transmit and receiving ACK from the target.
Each member sends these two statistics to the Management Center at intervals of 3 seconds (update interval). Management Center derives Events Published per Second and Average Event Latency from these statistics as formulated below:
Events Published per Second = (Current TBEC - Previous TBEC) / Update Interval
Average Event Latency = (Current TL - Previous TL) / (Current TBEC - Previous TBEC)
| Outbound Queue Fill Ratio is only available for version 5 and later of Hazelcast Platform clusters. Outbound Queue Fill Ratio may briefly go over 100% if the outbound queue overflows. |
Change WAN publisher state
A WAN publisher can be in one of the following states:
-
Replicating (default): State where both enqueuing new events are allowed; enqueued events are replicated to the target cluster.
-
Paused: State where new events are enqueued but are not dequeued. Some events which have been dequeued before the state was switched may still be replicated to the target cluster, but further events will not be replicated.
-
Stopped: State where neither new events are enqueued nor dequeued. As with the Paused state, some events might still be replicated after the publisher has switched to this state.
-
Mixed: Applicable only to a replication or a publisher, not applicable to a publisher member. State when members do not have the same state. For instance, two members are replicating and one member is paused.
To change a WAN publisher’s state, click the Change State dropdown button on top right corner of the WAN Publisher Table.
WAN sync
You can initiate a synchronization operation on a map for a specific target cluster. This operation is useful if two remote clusters lost their synchronization due to WAN queue overflow or in restart scenarios.
Hazelcast provides the following synchronization options:
-
Default WAN synchronization operation: All the data of a map is sent to a target cluster to align the state of the target map with the source map. See Synchronizing WAN Clusters for more information.
-
WAN synchronization using Merkle trees: To initiate this type of synchronization, you need to configure the cluster members. See Delta WAN Synchronization in the Hazelcast documentation for details about configuring them. Make sure you meet all the requirements to use Delta WAN Synchronization and perform the configuration on both the source and target clusters.
To initiate WAN Sync, open the WAN Replication menu item on the left and navigate to the Sync tab.
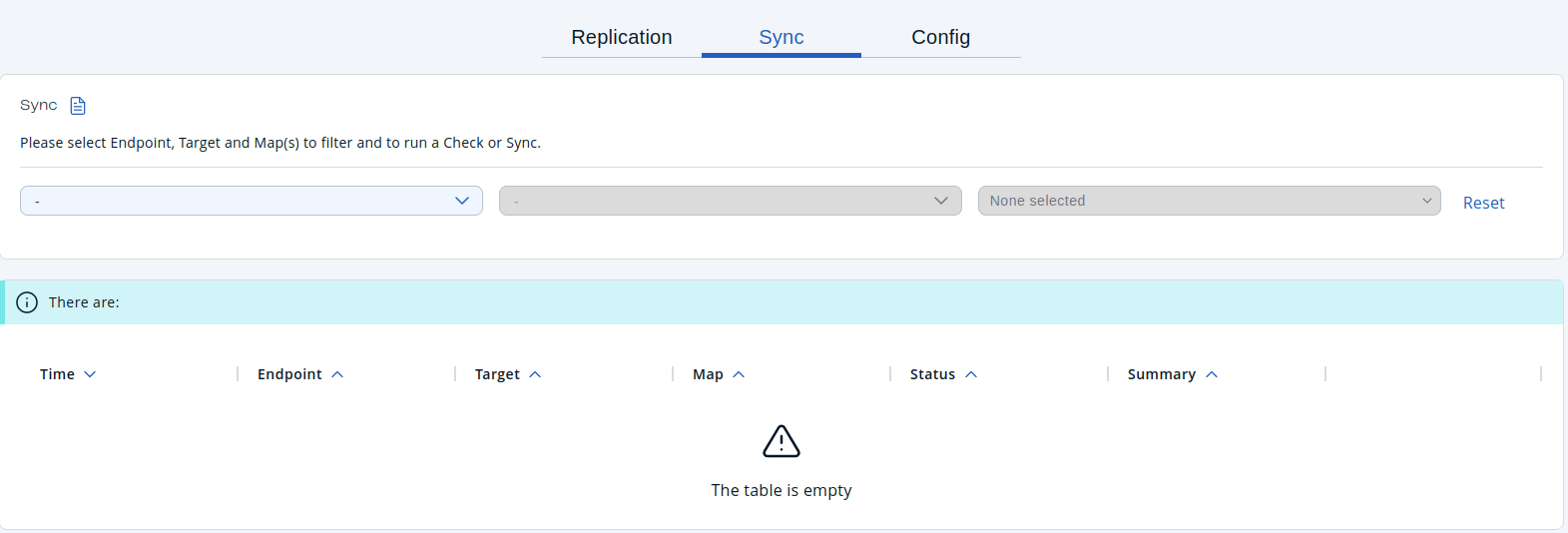
Select Endpoint(replication config), Target(publisher), and one or more Maps(configured with the selected replication) and click Sync to start the operation.
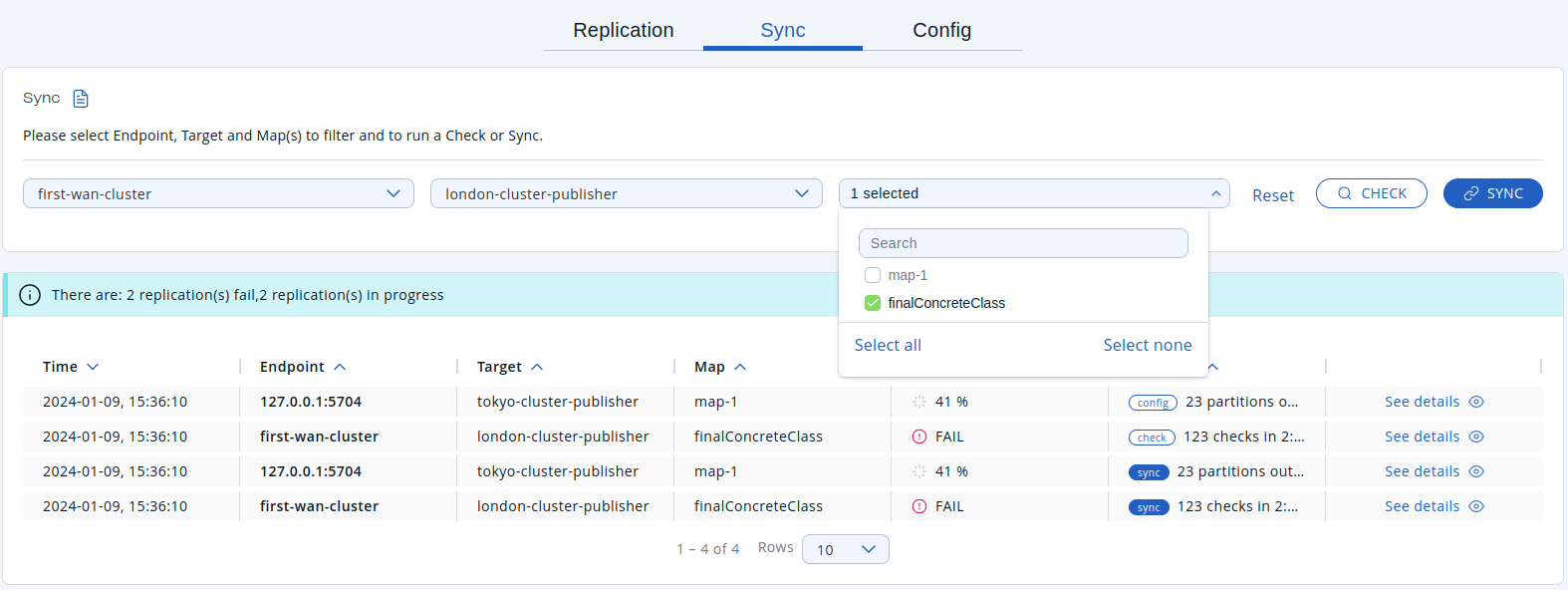
You can also use the Select All option in the Maps dropdown to synchronize all the maps in source and target cluster.
Once you initiate the sync, you’ll see the WAN Sync status entry shown in the table below:
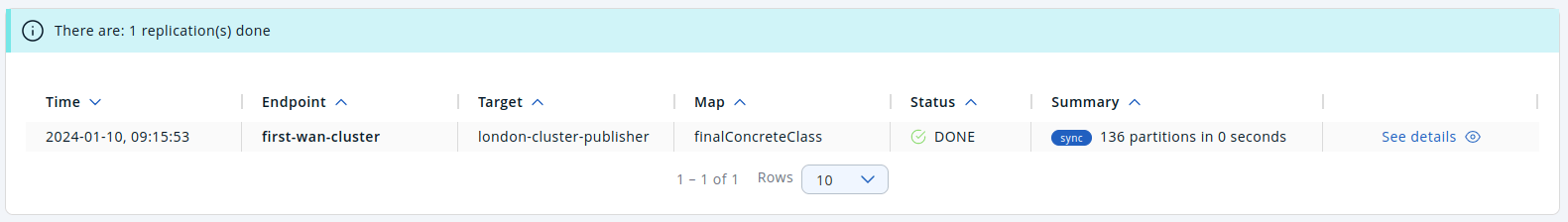
To see the progress of the sync, click on See details.
WAN Consistency Check
You can check if a map is in sync with a specific target cluster.
Configure the same options as for the WAN Sync and click
CHECK to start the operation.
You can see the WAN Sync status entry in the table below once you initiate the sync:
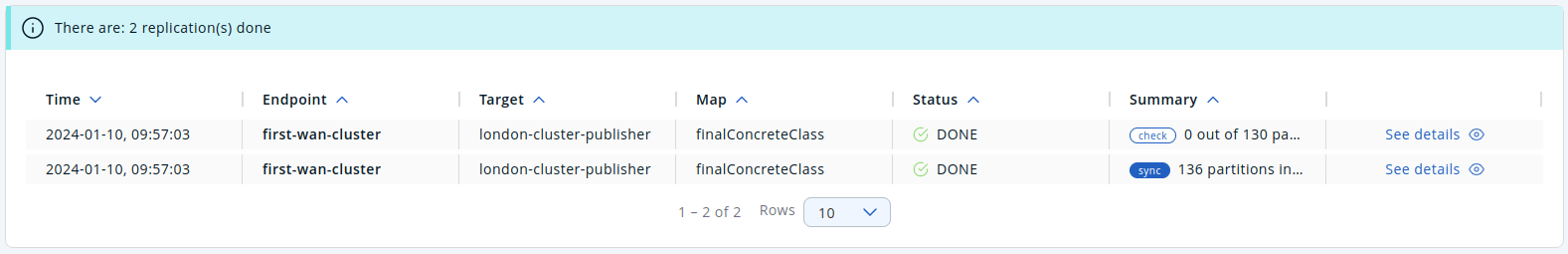
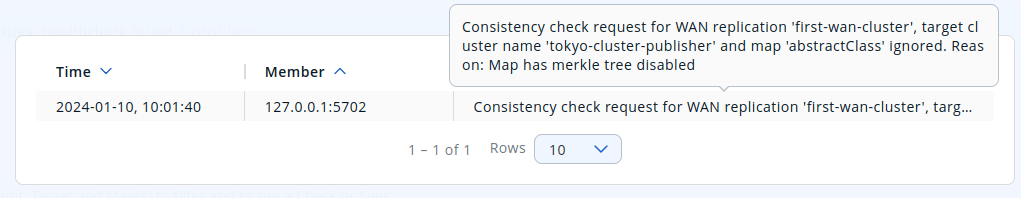
You can see the details of the consistency check if you click on See details:

| You need to use Merkle trees for WAN synchronization to check for consistency between two clusters. You must configure the Merkle trees on both the source and target clusters. If you do not configure it for the source cluster, consistency check is ignored. If it’s enabled for the source cluster but not for the target cluster, all entries are reported as if they need a sync, because a sync operation will be a full sync in the absence of Merkle trees. |
Add temporary WAN replication configuration
You can add a temporary WAN replication configuration dynamically to a cluster. It is useful for having one-off WAN sync operations. The added configuration is not persistent, so it does not survive a member restart.
If you configure a data structure to use the new WAN configuration, entries added after the configuration change are automatically replicated by the new WAN replication configuration.
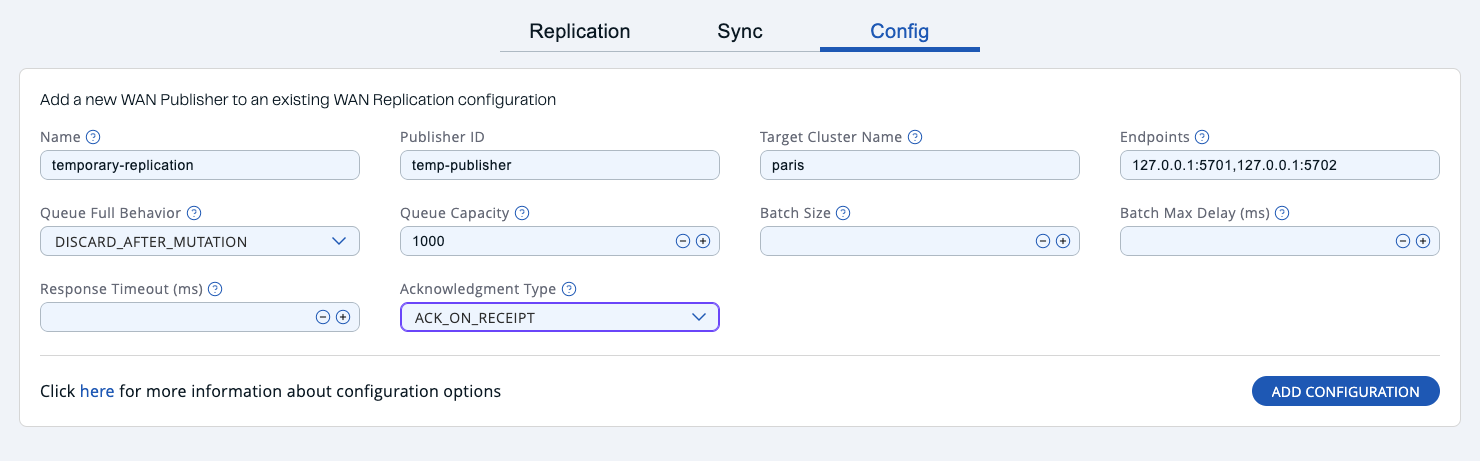
After clicking the Add Configuration button, the new WAN replication configuration is added to the cluster. You can see the new configuration when you try to initiate a WAN sync operation, as described in the previous section.
Related resources
For details about this feature, see WAN Replication in the Platform documentation.
