Hazelcast IMDG Reference Manual 3.12.13
Welcome to the Hazelcast IMDG (In-Memory Data Grid) Reference Manual. This manual includes concepts, instructions and examples to guide you on how to use Hazelcast and build Hazelcast IMDG applications.
This reference manual mostly talks about the Hazelcast member and clients in Java language. Although, the core of Hazelcast IMDG is based on the Java programming language, it has the following clients and programming language APIs.
-
Java
-
.NET
-
C++
-
Node.js
-
Python
-
Go
We recommend you to learn the basics of Hazelcast IMDG using this manual first. Then, you can always get the client related resources/links in the Clients chapter.
Editions
This Reference Manual covers all editions of Hazelcast IMDG. Throughout this manual:
-
Hazelcast or Hazelcast IMDG refers to the open source edition of Hazelcast in-memory data grid middleware. Hazelcast is also the name of the company (Hazelcast, Inc.) providing the Hazelcast product.
-
Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise is a commercially licensed edition of Hazelcast IMDG which provides high-value enterprise features in addition to Hazelcast IMDG.
-
Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise HD is a commercially licensed edition of Hazelcast IMDG which provides High-Density (HD) Memory Store and Hot Restart Persistence features in addition to Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise.
Hazelcast IMDG Architecture
You can see the features for all Hazelcast IMDG editions in the following architecture diagram.
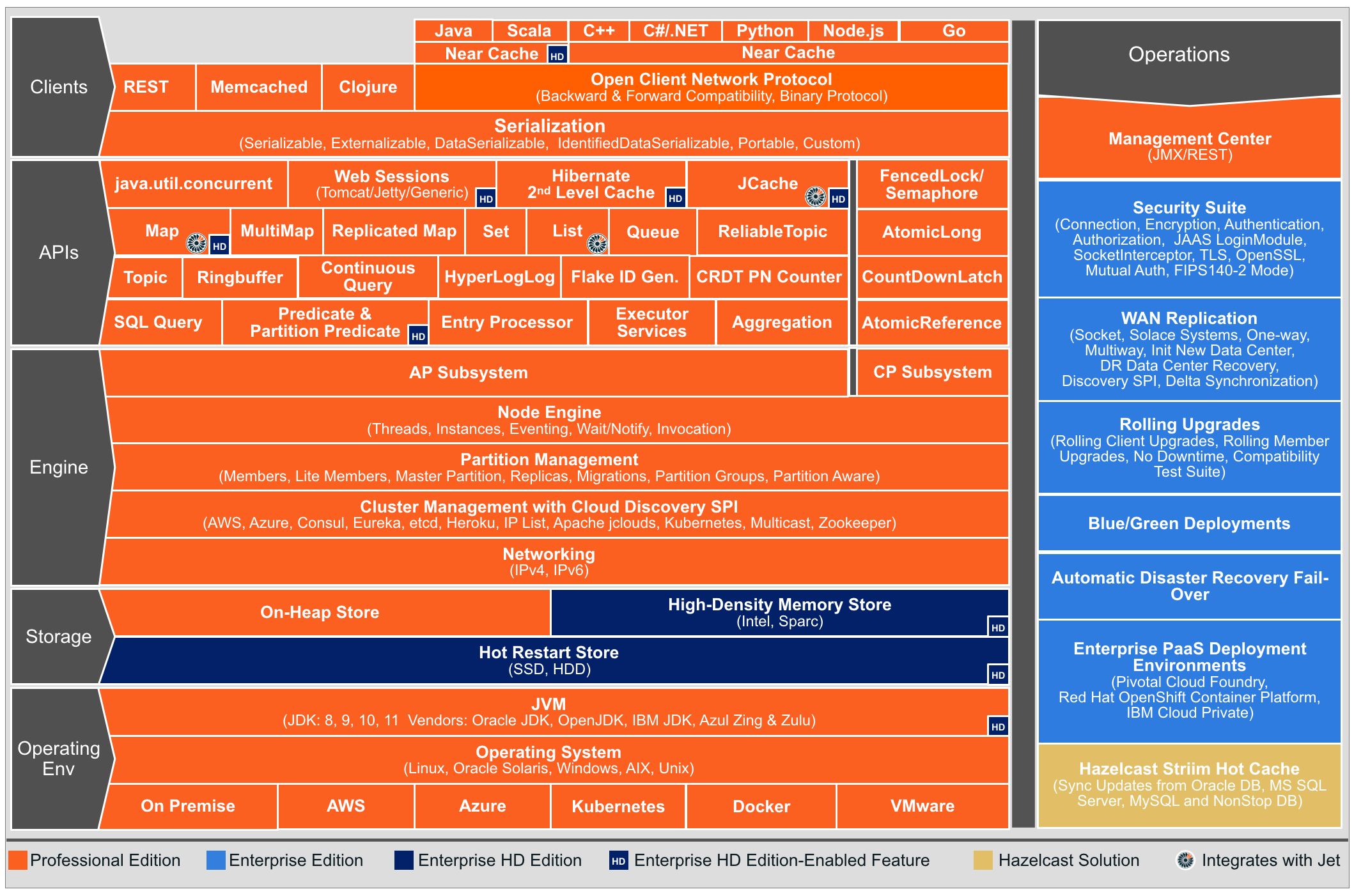
| You can see small "HD" boxes for some features in the above diagram. Those features can use High-Density (HD) Memory Store when it is available. It means if you have Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise HD, you can use those features with HD Memory Store. |
For more information on Hazelcast IMDG’s Architecture, see the white paper An Architect’s View of Hazelcast.
Hazelcast IMDG Plugins
You can extend Hazelcast IMDG’s functionality by using its plugins. These plugins have their own lifecycles. See the Plugins page to learn about Hazelcast plugins you can use. Hazelcast plugins are marked with ![]() label throughout this manual. See also the Hazelcast Plugins chapter for more information.
label throughout this manual. See also the Hazelcast Plugins chapter for more information.
Licensing
Hazelcast IMDG and Hazelcast Reference Manual are free and provided under the Apache License, Version 2.0. Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise and Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise HD is commercially licensed by Hazelcast, Inc.
For more detailed information on licensing, see the License Questions appendix.
Trademarks
Hazelcast is a registered trademark of Hazelcast, Inc. All other trademarks in this manual are held by their respective owners.
Customer Support
Support for Hazelcast is provided via GitHub, Mail Group and StackOverflow.
For information on the commercial support for Hazelcast IMDG and Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise, see hazelcast.com.
Release Notes
See the Release Notes document for the new features, enhancements and fixes performed for each Hazelcast IMDG release.
Contributing
You can contribute to the Hazelcast IMDG code, report a bug, or request an enhancement. See the following resources:
-
Developing with Git: Document that explains the branch mechanism of Hazelcast and how to request changes.
-
Hazelcast on GitHub: Hazelcast repository where the code is developed, issues and pull requests are managed.
Partners
Hazelcast partners with leading hardware and software technologies, system integrators, resellers and OEMs including Amazon Web Services, Vert.x, Azul Systems, C2B2. See the Partners page for the full list of and information on our partners.
Phone Home
Hazelcast uses phone home data to learn about usage of Hazelcast IMDG.
Hazelcast IMDG member instances call our phone home server initially when they are started and then every 24 hours. This applies to all the instances joined to the cluster.
What is sent in?
The following information is sent in a phone home:
-
Hazelcast IMDG version
-
Local Hazelcast IMDG member UUID
-
Download ID
-
A hash value of the cluster ID
-
Cluster size bands for 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 100, 150, 300, 600 and > 600
-
Number of connected clients bands of 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 100, 150, 300, 600 and > 600
-
Cluster uptime
-
Member uptime
-
Environment Information:
-
Name of operating system
-
Kernel architecture (32-bit or 64-bit)
-
Version of operating system
-
Version of installed Java
-
Name of Java Virtual Machine
-
-
Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise specific:
-
Number of clients by language (Java, C++, C#)
-
Flag for Hazelcast Enterprise
-
Hash value of license key
-
Native memory usage
-
-
Hazelcast Management Center specific:
-
Hazelcast Management Center version
-
Hash value of Hazelcast Management Center license key
-
Phone Home Code
The phone home code itself is open source. See the code here.
Disabling Phone Homes
Set the hazelcast.phone.home.enabled system property to false either in the config or on the Java command line. See the System Properties appendix for information on how to set a property.
You can also disable the phone home using the environment variable HZ_PHONE_HOME_ENABLED. Simply add the following line to your .bash_profile:
export HZ_PHONE_HOME_ENABLED=falsePhone Home URLs
For versions 1.x and 2.x: http://www.hazelcast.com/version.jsp.
For versions 3.x up to 3.6: http://versioncheck.hazelcast.com/version.jsp.
For versions after 3.6: http://phonehome.hazelcast.com/ping.
