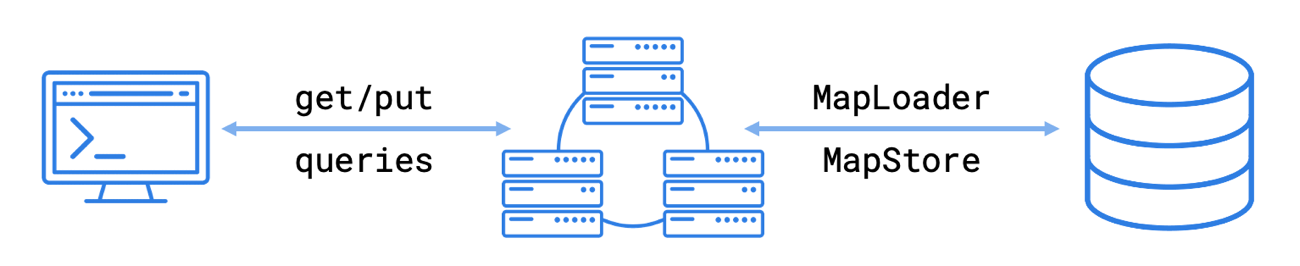
MapStore is an API for building a cache on top of Hazelcast. The MapStore interface includes methods that are triggered when operations are invoked on a map. MapStores connect to a data store, load data from it, and write data back to it. For example, you can use a MapStore to load data into your cluster from a MongoDB, MySQL, or PostgreSQL database.
Hazelcast comes with a generic MapStore that requires little to no Java code as well as a custom option that allows you to write the implementation yourself.
Supported Caching Patterns
MapStore supports the following caching patterns:
-
Read-through (always): If an entry does not exist in memory when an application asks for it, Hazelcast asks the MapStore implementation to load that entry from the data store. If the entry exists, the MapStore implementation requests it from the data store and Hazelcast puts it into memory.
-
Write-through (default): When new entries are added to a map, those entries are added to the data store synchronously.
-
Write-behind (requires configuration): When new entries are added to a map, those entries are added to the data store asynchronously, after a configured delay.
Options for Building a MapStore
To build a cache using a MapStore, you need an implementation of the MapStore or MapLoader interface. Hazelcast comes with a generic MapStore that requires little to no Java code as well as a custom option that allows you to write the implementation yourself.
Generic MapStore
The generic MapStore is a pre-built implementation that connects to an external data store, using the external-data-store configuration.
The generic MapStore is called low-code because it requires you to write little to no Java code:
-
If Hazelcast provides a built-in data store factory for your data store, you can configure your cluster to use it, without writing any Java code.
-
If Hazelcast doesn’t provide a built-in data store factory for your data store, you can write your own in Java to allow the pre-built MapStore to connect to your data store.
