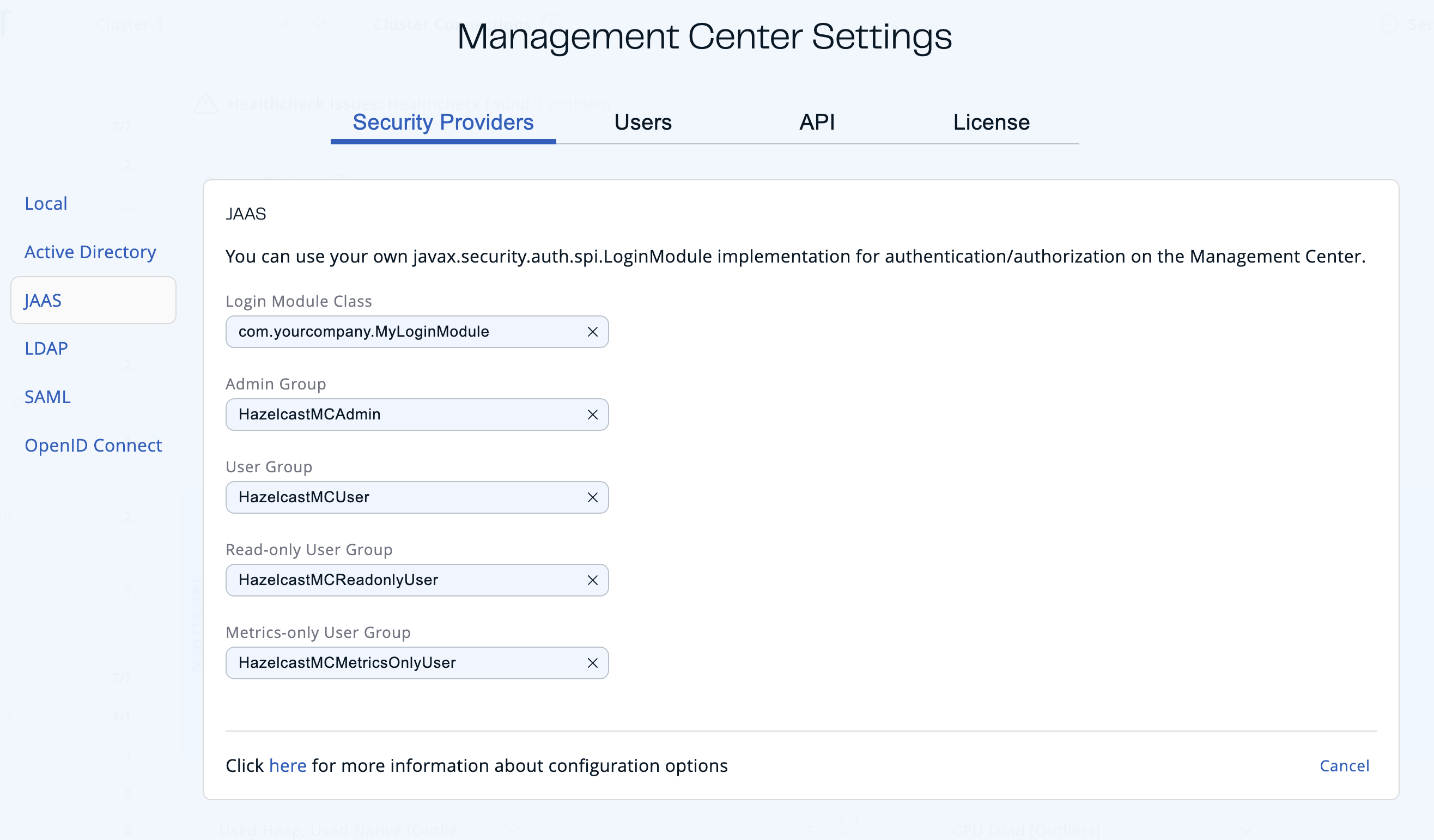
JAAS
You can use your own `javax.security.auth.spi.LoginModule` implementation for authentication and authorization in Management Center.
Set up the JAAS security provider
To set up JAAS, you need to configure settings either in the UI or the hz-mc conf tool.
You must be an admin user.
To set up the local security provider in the UI, go to Settings > Security Providers > JAAS.
Use the jaas configure task. For help, use the -h flag or see Management Center Configuration Tool.
hz-mc conf jaas configuremc-conf.bat jaas configure-
Login Module Class: Fully qualified class name of your
javax.security.auth.spi.LoginModuleimplementation. -
Admin Group: Members of this group have admin privileges on the Management Center.
-
User Group: Members of this group have read and write privileges on the Management Center.
-
Read-only User Group: Members of this group have only read privilege on the Management Center.
-
Metrics-only Group: Members of this group have the privilege to see only the metrics on the Management Center.
Create and manage users
To create and manage additional users, you must configure them in your JAAS login module.
When creating users, be sure to give them a valid role. See User management.
The following is an example implementation. Note that this example returns two java.security.Principal
instances; one of them is the username and the other one is a group name, which
you will use when configuring JAAS security as described above.
import javax.security.auth.Subject;
import javax.security.auth.callback.Callback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.CallbackHandler;
import javax.security.auth.callback.NameCallback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.PasswordCallback;
import javax.security.auth.login.LoginException;
import javax.security.auth.spi.LoginModule;
import java.security.Principal;
import java.util.Map;
public class SampleLoginModule implements LoginModule {
private Subject subject;
private String password;
private String username;
@Override
public void initialize(Subject subject, CallbackHandler callbackHandler, Map<String, ?> sharedState, Map<String, ?> options) {
this.subject = subject;
try {
NameCallback nameCallback = new NameCallback("prompt");
PasswordCallback passwordCallback = new PasswordCallback("prompt", false);
callbackHandler.handle(new Callback[] {nameCallback, passwordCallback });
password = new String(passwordCallback.getPassword());
username = nameCallback.getName();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public boolean login() throws LoginException {
if (!username.equals("emre")) {
throw new LoginException("Bad User");
}
if (!password.equals("pass1234")) {
throw new LoginException("Bad Password");
}
subject.getPrincipals().add(new Principal() {
public String getName() {
return "emre";
}
});
subject.getPrincipals().add(new Principal() {
public String getName() {
return "HazelcastMCAdmin";
}
});
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean commit() throws LoginException {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean abort() throws LoginException {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean logout() throws LoginException {
return true;
}
}Next steps
For details about the hz-mc conf tool, see Management Center Configuration Tool.

