Use Hazelcast Cloud to process streaming data, enrich streaming data with data in fast storage, store output in fast storage, and use an entry processor to update inventory.
Context
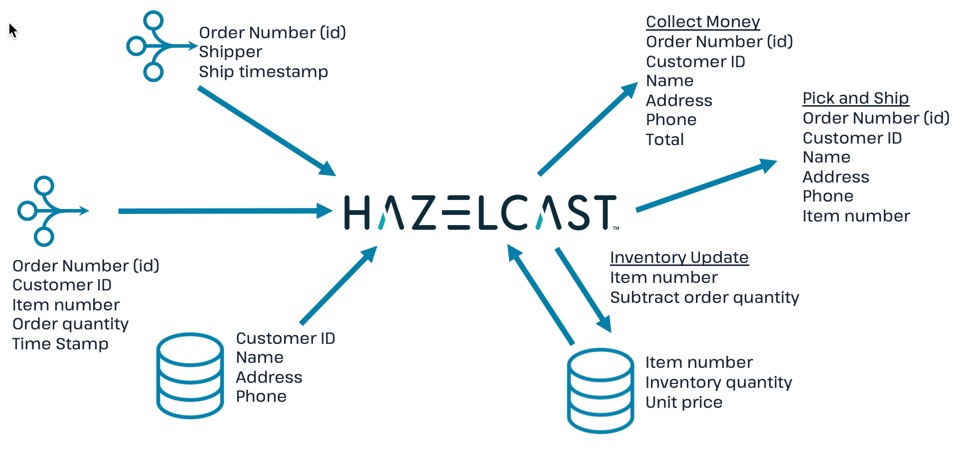
In this tutorial, you will build, step by step, a simple e-commerce order processing application.
Step 1: Connect to a streaming source. Step 2: Import customer and inventory databases. Step 3: Generate pick-and-ship order Step 4: Generate info for money collection Step 5: Generate shipping confirmation Step 6: Update inventory count
Before you Begin
This tutorial is designed to be completed in conjunction with the Hazelcast Platform Essentials course. Although you can complete this tutorial independently, the course provides operational context and additional information on Hazelcast.
Before starting this tutorial, make sure that you meet the following prerequisites:
-
Connect the Command Line Client or open the SQL tab for your cluster
-
Download the repository at https://github.com/hazelcast-guides/Stream-Processing-Intro
Step 1. Connect to Streaming Source
In this step, you will set up connections to an external streaming source and an external database.
-
If you are using the cloud dashboard, open an SQL tab. If you are using the Command Line Client (CLC), open the CLC connection to your cloud cluster.
Cloud:
CLC:
Your screen or prompt will display your cluster name where the examples above say "EdSrvs1".
-
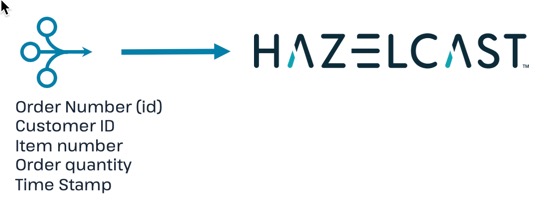
Paste the following code to establish a connection to the streaming data source.
CREATE OR REPLACE DATA CONNECTION TrainingKafkaConnection TYPE Kafka NOT SHARED OPTIONS ('bootstrap.servers'='35.88.250.10:9092', 'security.protocol'='SASL_PLAINTEXT', 'client.dns.lookup'='use_all_dns_ips', 'sasl.mechanism'='SCRAM-SHA-512', 'sasl.jaas.config'='org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="training_ro" password="h@zelcast!";', 'session.timeout.ms'='45000' ); -
Paste the following code to subscribe to the streaming topic for sales data.
CREATE OR REPLACE MAPPING "orders_topic" EXTERNAL NAME "stream_processing_intro.orders" ( id bigint, order_time timestamp with time zone, cust_id varchar, item_num varchar, quantity int ) DATA CONNECTION "TrainingKafkaConnection" OPTIONS ( 'keyFormat' = 'varchar', 'valueFormat' = 'json-flat' ); -
Verify that you are receiving streaming data from the topic
orders_topic.SELECT * from orders_topic;If you are using the query tab, press Execute Query. If you are using CLC, press enter to start the query.
-
Stop the query. If you are using the query tab press Stop Query. If you are using CLC, press CTRL-C.
Step 2. Load Fast Data Store

In this step, you’ll load the in-memory data stores that will be used for stream enrichment and for inventory tracking. The data is currently stored in an external Postgres database, and we need to move it to local memory for fast access.
-
Connect to the Postgres server.
CREATE OR REPLACE DATA CONNECTION TrainingPostgresConnection TYPE JDBC SHARED OPTIONS ('jdbcUrl'='jdbc:postgresql://training.cpgq0s6mse2z.us-west-2.rds.amazonaws.com:5432/postgres', 'user'='training_ro', 'password'='h@zelcast!' ); -
Create the mapping for the customer database stored in the Postgres server.
CREATE OR REPLACE MAPPING "external_customers" EXTERNAL NAME "stream_processing_intro"."customers" ( cust_id VARCHAR, last_name VARCHAR, first_name VARCHAR, address1 VARCHAR, address2 VARCHAR, phone VARCHAR ) DATA CONNECTION "TrainingPostgresConnection"; -
Create the mapping for the IMap that will store the local copy of the customer database. Note that the data fields are identical.
CREATE OR REPLACE MAPPING "customers"( cust_id VARCHAR, last_name VARCHAR, first_name VARCHAR, address1 VARCHAR, address2 VARCHAR, phone VARCHAR ) Type IMap OPTIONS ( 'keyFormat' = 'varchar', 'valueFormat' = 'json-flat' ); -
Verify that the local IMap is currently empty.
SELECT * from customers; -
Copy the data from the external database to the local IMap.
INSERT INTO customers(__key, cust_id, last_name, first_name, address1, address2, phone) -- use cust_id for __key as well as first field in value SELECT cust_id, cust_id, last_name, first_name, address1, address2, phone FROM external_customers; -
Verify that the data has been added to the
customersmap.SELECT * FROM customers;You should see the complete list of customers.
-
Create the mapping for the external inventory database.
CREATE OR REPLACE MAPPING "external_inventory" EXTERNAL NAME "stream_processing_intro"."inventory" ( item_num VARCHAR, unit_price DECIMAL, quantity SMALLINT ) DATA CONNECTION "TrainingPostgresConnection"; -
Create the mapping for the IMap that will store the local copy of the inventory.
CREATE or REPLACE MAPPING "inventory" ( __key VARCHAR, item_num VARCHAR, unit_price DECIMAL, quantity SMALLINT) TYPE IMap OPTIONS ( 'keyFormat'='varchar', 'valueFormat'='json-flat'); -
Copy the inventory data from the external database into the IMap
INSERT INTO inventory(__key, item_num, unit_price, quantity) -- use item_num as key as well as first field in value SELECT item_num, item_num, unit_price, quantity FROM external_inventory; -
Verify that the data has been added to the
inventorydatabase.SELECT * from inventory;
Step 3: Generate Warehouse Pick Order
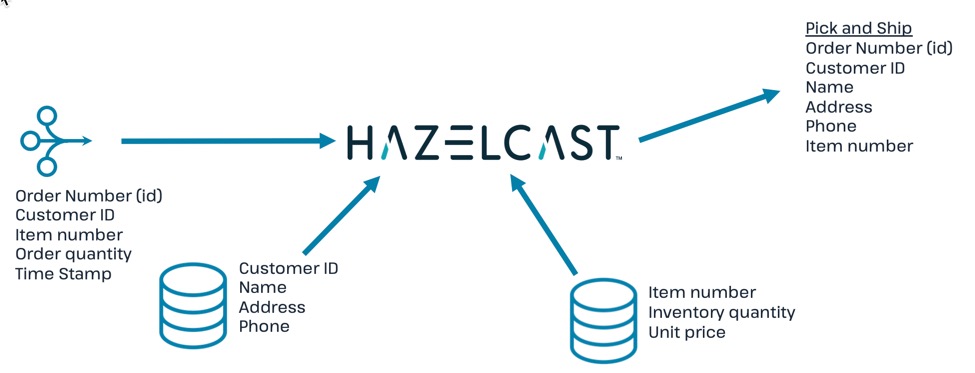
In this step, you will join the streaming order information with the customer shipping data to generate a pick and ship order for the inventory warehouse.
-
Create an IMap to store pick order data.
CREATE OR REPLACE MAPPING PickOrder ( __key BIGINT, ts TIMESTAMP, item_num VARCHAR, quantity SMALLINT, cust_id VARCHAR, last_name VARCHAR, first_name VARCHAR, address1 VARCHAR, address2 VARCHAR, phone VARCHAR) TYPE IMap OPTIONS ( 'keyFormat'='bigint', 'valueFormat'='json-flat'); -
Verify that the IMap has been created, but holds no data.
SELECT * FROM PickOrder; -
Join the streaming order data with the customer database to produce records to be added to the
PickOrderIMap. Only add records if there are sufficient items in inventory.The following fields will come from the
orders_topicstream-
Order ID (Use as __key for the IMap)
-
Order timestamp
-
Order item number
-
Order quantity
-
Customer ID
The following fields will come from the
customersdata store. -
Customer last name
-
Customer first name
-
Customer address line 1
-
Customer address line 2
-
Customer phone number
The common data field between
ordersandcustomersiscust_id.The common data field between
ordersandinventoryisitem_num.
SELECT ord.id AS __key, ord.order_time AS ts, ord.item_num AS item_num, ord.quantity AS quantity, ord.cust_id AS cust_id, cust.last_name AS last_name, cust.first_name AS first_name, cust.address1 AS address1, cust.address2 AS address2, cust.phone AS phone FROM orders_topic AS ord JOIN customers AS cust ON ord.cust_id = cust.cust_id JOIN inventory ON ord.item_num = inventory.item_num WHERE ord.quantity < inventory.quantity; -
-
Press CTRL-C to stop the join.
-
Create a job that generates the PickOrder. Creating a job places the process into the background so it is running continuously without user intervention.
CREATE JOB PickOrder AS SINK INTO PickOrder SELECT ord.id AS __key, ord.order_time AS ts, ord.item_num AS item_num, ord.quantity AS quantity, ord.cust_id AS cust_id, cust.last_name AS last_name, cust.first_name AS first_name, cust.address1 AS address1, cust.address2 AS address2, cust.phone AS phone FROM orders_topic AS ord JOIN customers AS cust ON ord.cust_id = cust.cust_id JOIN inventory ON ord.item_num = inventory.item_num WHERE ord.quantity < inventory.quantity; -
Verify that the
PickOrderIMap now contains data.SELECT * FROM PickOrder; -
From your cloud console, monitor memory utilization. You should see it increasing.
-
From Management Center, under Storage, select Maps. You should see the PickOrder map entries increasing.
-
From Management Center, under Streaming, select Jobs. You should see the PickOrder job running. Select the job, then click the Suspend button to pause the job.
Step 4: Generate Order Total
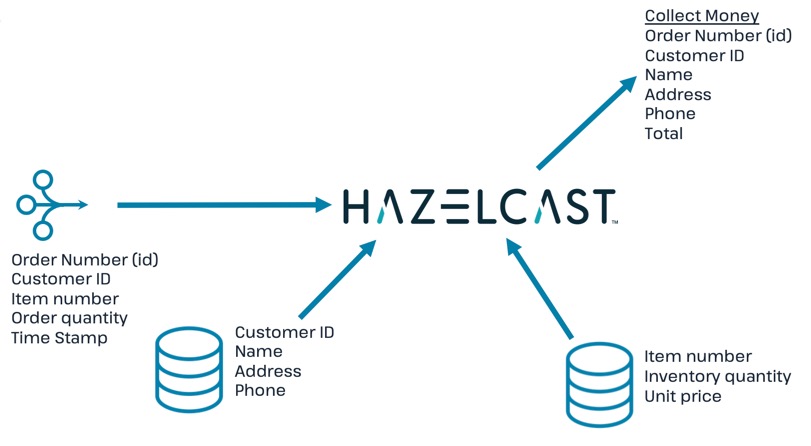
In this step, you will perform a three-way join with the streaming order information, the customer database, and the inventory database. The output includes a calculation of the amount due for the order, and is passed to an IMap. This map can then be read by a payment processing system.
-
Create a new IMap called
amount_due.CREATE OR REPLACE MAPPING amount_due( __key BIGINT, cust_id VARCHAR, last_name VARCHAR, first_name VARCHAR, address1 VARCHAR, address2 VARCHAR, phone VARCHAR, total DECIMAL) TYPE IMap OPTIONS ( 'keyFormat' = 'bigint', 'valueFormat' = 'json-flat'); -
Join the order stream and the customer database to generate the amount due information and publish it to the
amount_duetopic you just created.CREATE JOB amount_due AS SINK INTO amount_due SELECT ord.id AS __key, ord.cust_id AS cust_id, cust.last_name AS last_name, cust.first_name AS first_name, cust.address1 AS address1, cust.address2 AS address2, cust.phone AS phone, (ord.quantity*inv.unit_price) AS total FROM orders_topic AS ord JOIN customers AS cust ON ord.cust_id = cust.cust_id JOIN inventory AS inv ON ord.item_num = inv.item_num; -
Verify that data is being published to the
amount_duemap.SELECT * FROM amount_due;
Step 5 (Optional): Examine Java Pipelines
Download the entire repository from GitHub: https://github.com/hazelcast-guides/Stream-Processing-Intro. Under the Sample Pipelines directory, you will find sample code that performs the same functions as the two pipelines you created in SQL. The supporting classes are also included.
