What You’ll Learn
In this tutorial, you will learn how to configure Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise to authenticate cluster members and clients using Kerberos tickets in the Microsoft Active Directory domain.
You will also cover the role mapping based on the user’s group membership in the Active Directory.
Before you Begin
-
Hazelcast IMDG Enterprise and its License Key (You can ask for a trial license through the license form).
-
Active Directory server (AD) and the 2nd Windows server connected in the Active Directory domain
-
JDK 1.8+ (You can get Windows installer on Azul Zulu download page for instance.)
-
A text editor or IDE
Active Directory domain in MS Azure
If you don’t have an Active Directory domain configured in your environment, you can provision one in MS Azure. There is an Azure deployment template on GitHub which starts a domain for you on few clicks:
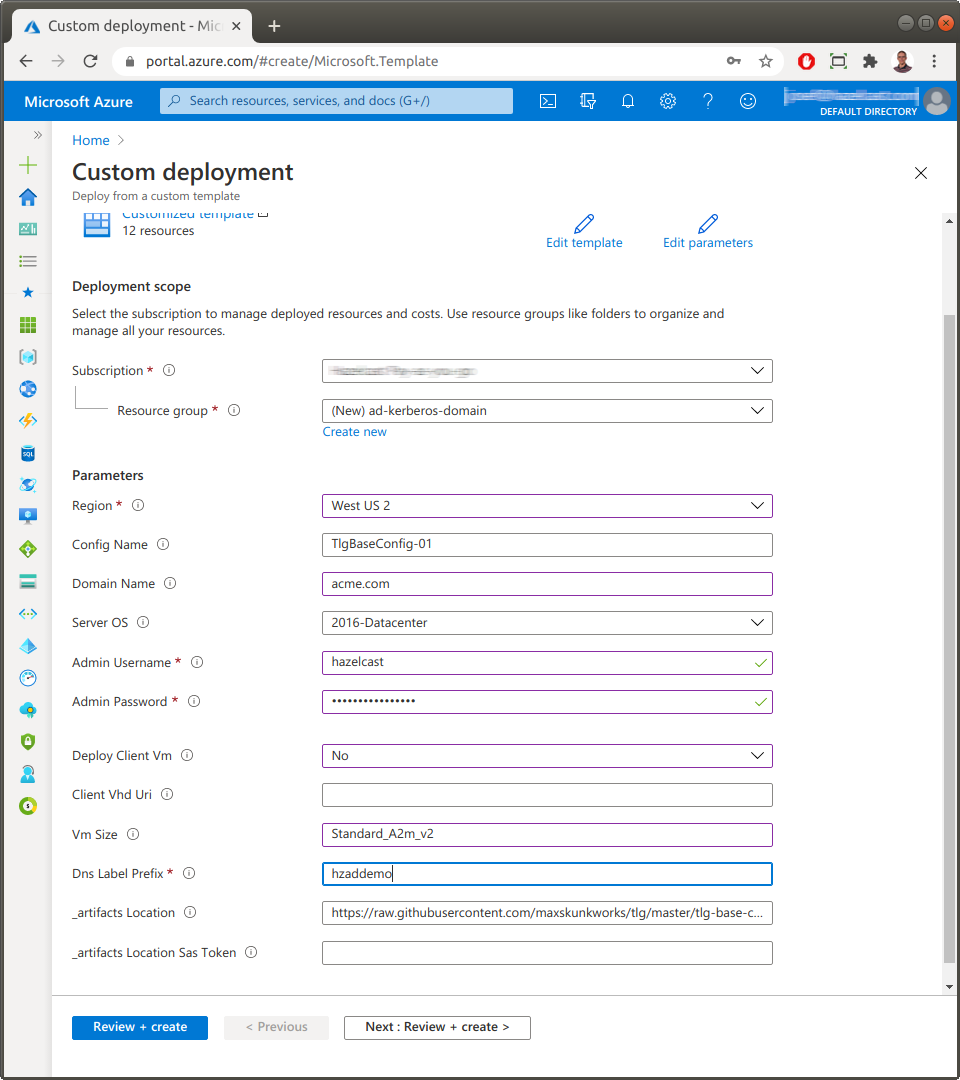
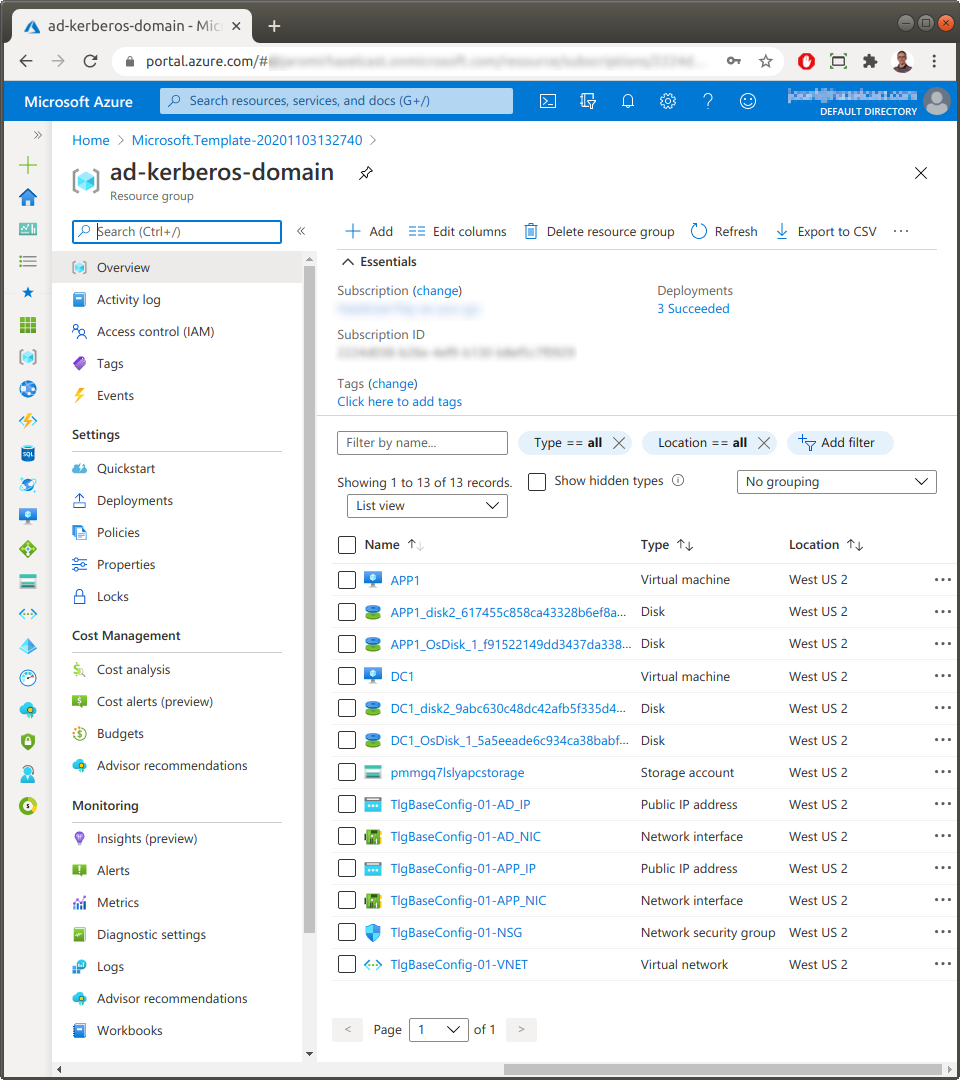
Environment
The sample environment used in this guide contains 2 Windows servers
-
Domain controller with Active Directory (hostname:
dc1) -
Application server attached to the domain (hostname:
app1)
The servers are connected to a domain named acme.com. Its upper-case version
is also the Kerberos realm name (ACME.COM).
Hazelcast connections are based on IP addresses, so they will be also necessary for the Kerberos authentication configuration.
Following addresses are used in our environment:
10.0.0.10 dc1
10.0.0.11 app1If you don’t use the Azure test environment, then replace the hostname and IP values to fit your environment in commands and Hazelcast configuration files used in this guide.
Hazelcast port on Windows Firewall
If you have Windows Firewall enabled, then allow access to the default Hazelcast
port numbers (5701-5703). You can use the following PowerShell command:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'Hazelcast ports 5701-5703' `
-Name Hazelcast -Direction Inbound -Action Allow `
-Protocol TCP -LocalPort 5701-5703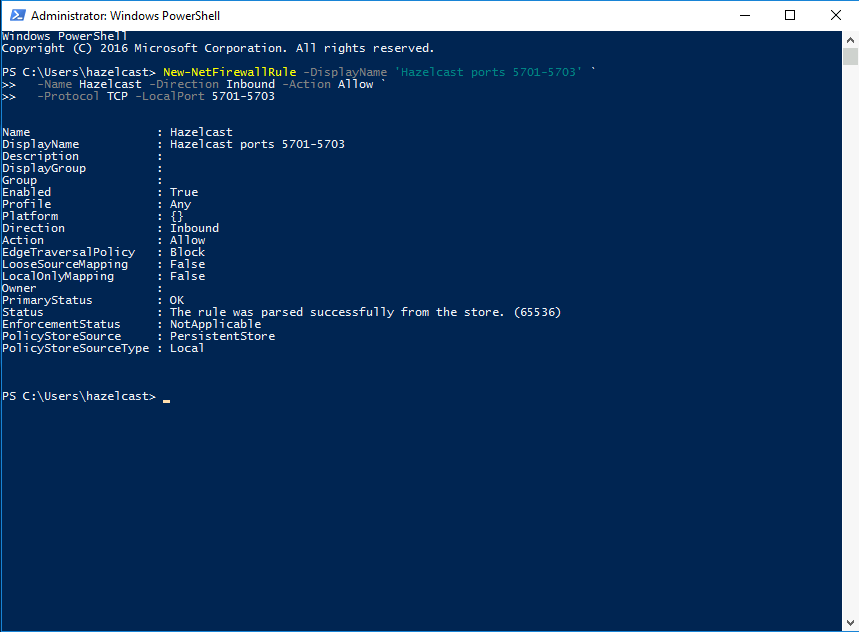
Kerberos configuration file
Java searches the Kerberos realms configuration in the krb5.ini file on Windows.
The file contains the address of the Key Distribution Center (KDC) - i.e. Active
Directory server in our case.
So let’s create one simple configuration file C:\Windows\krb5.ini
on both servers.
[libdefaults]
default_realm = ACME.COM
[realms]
ACME.COM = {
kdc = dc1.acme.com
}
[domain_realm]
.acme.com = ACME.COM| Kerberos protocol checks are often case-sensitive. Use the proper form of principal names and use the upper-case Kerberos realm name! |
Create member accounts in Active Directory
We will use the PowerShell on the Domain controller to create an Active Directory user account for each Hazelcast member. We don’t need to provide passwords, Active Directory will generate random ones for us. We will also need a keytab file for each member. Keytab files will contain the password as a shared secret used for authentication and Kerberos ticket verification.
New-ADUser -Name hz-app1 -PasswordNotRequired $True `
-PasswordNeverExpires $True -PassThru -Enabled $True
ktpass -princ hz/[email protected] -mapuser [email protected] `
-out hz-app1.keytab +rndPass -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL
New-ADUser -Name hz-dc1 -PasswordNotRequired $True `
-PasswordNeverExpires $True -PassThru -Enabled $True
ktpass -princ hz/[email protected] -mapuser [email protected] `
-out hz-dc1.keytab +rndPass -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPALCommands used:
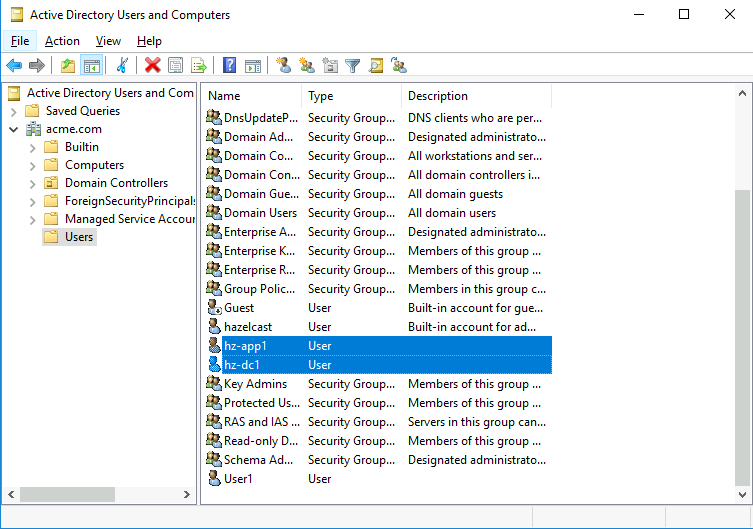
The hz/[email protected] and hz/[email protected] are Service Principal Names (SPN)
and we will reference them in the Hazelcast member configuration.
The hz/ is a service prefix, followed by the IP address and the Kerberos realm name.
Move the newly generated keytab files to the bin directory within the Hazelcast
Enterprise installation (e.g. C:\hazelcast-enterprise-4.1\bin).
As the hz-app1 account will be used by the application server we need to
move the newly generated hz-app1.keytab file from the domain controller
to the application server.
|
Configure Hazelcast members
We will use the YAML configuration file located in the bin directory.
We need to remove the existing member configuration file (hazelcast.xml) first.
cd \hazelcast-enterprise-4.1\bin
del hazelcast.xmlNow we create the new configuration file called hazelcast.yml.
The file will define the network discovery method and security.
The simple form of Kerberos security configuration will be used - this should only be used for testing.
Following configuration is for the application server:
hazelcast:
license-key: "PUT_THE_LICENSE_KEY_HERE"
network:
join:
multicast:
enabled: false
tcp-ip:
enabled: true
member-list:
- 10.0.0.10
- 10.0.0.11
security:
enabled: true
realms:
- name: kerberosRealm
authentication:
kerberos:
relax-flags-check: true
use-name-without-realm: true
principal: hz/[email protected]
keytab-file: hz-app1.keytab
identity:
kerberos:
realm: ACME.COM
principal: hz/[email protected]
keytab-file: hz-app1.keytab
member-authentication:
realm: kerberosRealmUse similar configuration on the domain controller. Just update principal name and path to the keytab file:
principal: hz/[email protected]
keytab-file: hz-dc1.keytabDon’t forget to replace
PUT_THE_LICENSE_KEY_HERE placeholder with a real license key.
Starting Hazelcast members on both servers should now result in forming a new Hazelcast cluster with both members.
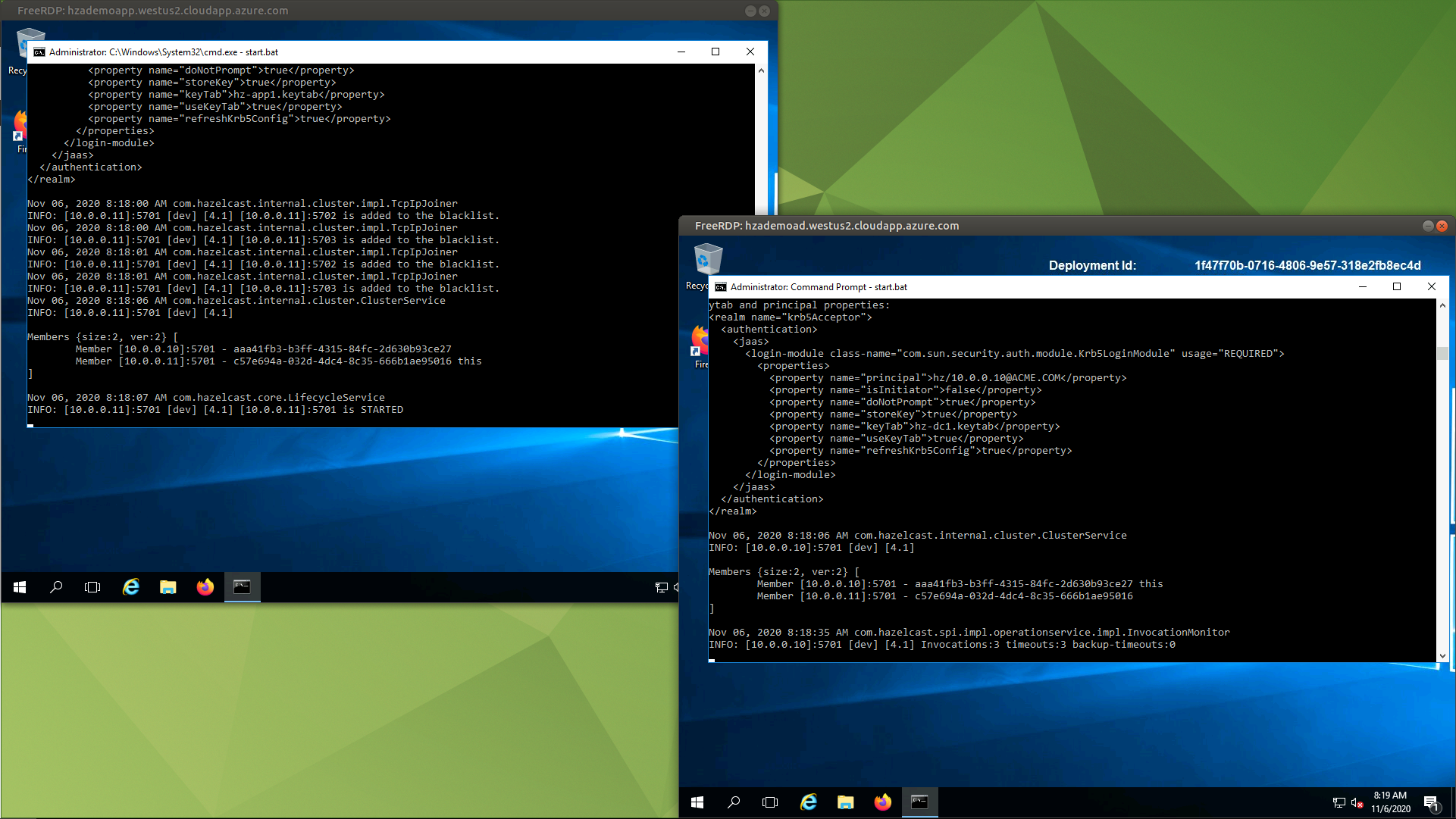
Within the security configuration, we defined which realm is used for
the member-to-member authentication (kerberosRealm).
The security realm itself has two configuration parts:
-
authentication- responsible for verifying incoming connections and mapping client roles; -
identity- defines a member’s credentials - used to prove its own identity to other members.
The most important options in the kerberos authentication and kerberos identity configurations
are the principal (defines own Kerberos name) and keytab-file (file containing secrets of
given principal).
Simple Kerberos configuration warnings
A warning message is printed to the console when the simple Kerberos configuration form is used for authentication. It gives us a hint on how to configure the full JAAS authentication.
WARNING: Using generated Kerberos initiator realm configuration is not intended for production use. It's recommended to properly configure the Krb5LoginModule manually to fit your needs. Following configuration was generated from provided keytab and principal properties:
<realm name="krb5Initiator">
<authentication>
<jaas>
<login-module class-name="com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule" usage="REQUIRED">
<properties>
<property name="principal">hz/[email protected]</property>
<property name="isInitiator">true</property>
<property name="doNotPrompt">true</property>
<property name="storeKey">true</property>
<property name="keyTab">hz-app1.keytab</property>
<property name="useKeyTab">true</property>
<property name="refreshKrb5Config">true</property>
</properties>
</login-module>
</jaas>
</authentication>
</realm>WARNING: Using generated Kerberos acceptor realm configuration is not intended for production use. It's recommended to properly configure the Krb5LoginModule manually to fit your needs. Following configuration was generated from provided keytab and principal properties:
<realm name="krb5Acceptor">
<authentication>
<jaas>
<login-module class-name="com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule" usage="REQUIRED">
<properties>
<property name="principal">hz/[email protected]</property>
<property name="isInitiator">false</property>
<property name="doNotPrompt">true</property>
<property name="storeKey">true</property>
<property name="keyTab">hz-dc1.keytab</property>
<property name="useKeyTab">true</property>
<property name="refreshKrb5Config">true</property>
</properties>
</login-module>
</jaas>
</authentication>
</realm>We will show how to use the full Kerberos configuration form in next sections.
Configure Hazelcast Client
Once we have the cluster running we will configure a client. Its roles will be loaded from the Active Directory using the LDAP protocol. We will use the existing domain user account for authenticating the client.
Create groups and mappings in Active Directory
To demonstrate the recursive role mapping feature, we will define two new
Active Directory groups. The first one, called "Acme Cache" will have its name
referenced in client permissions configuration on Hazelcast members.
The second group "Acme Cache Czechia" will be a member of the first one.
The active domain user (hazelcast in our environment) will be added
as a member of the "Acme Cache Czechia" group.
New-ADGroup -Name "Acme Cache" -GroupScope Global `
-Description "Cache users"
New-ADGroup -Name "Acme Cache Czechia" -GroupScope Global `
-Description "Cache users in the Czech Republic"
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity "Acme Cache" -Members "Acme Cache Czechia"
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity "Acme Cache Czechia" -Members hazelcastRe-configure members
We used the simplified Kerberos configuration when we tried Kerberos authentication between members. Let’s use the full form now. We need it also to enable Kerberos (GSS-API) authentication into Active Directory’s LDAP interface.
hazelcast:
license-key: "PUT_THE_LICENSE_KEY_HERE"
network:
join:
multicast:
enabled: false
tcp-ip:
enabled: true
member-list:
- 10.0.0.10
- 10.0.0.11
security:
enabled: true
realms:
- name: kerberosRealm
authentication:
kerberos:
relax-flags-check: true
use-name-without-realm: true
security-realm: krb5Acceptor
ldap:
url: ldap://DC1.acme.com/
system-authentication: GSSAPI
security-realm: krb5Initiator
skip-authentication: true
user-context: DC=acme,DC=com
user-filter: "(|(sAMAccountName={login})(servicePrincipalName={login}))"
role-mapping-mode: direct
role-mapping-attribute: memberOf
role-recursion-max-depth: 5
role-name-attribute: CN
parse-dn: false
identity:
kerberos:
realm: ACME.COM
security-realm: krb5Initiator
- name: krb5Acceptor
authentication:
jaas:
- class-name: com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule
usage: REQUIRED
properties:
isInitiator: false
useTicketCache: false
doNotPrompt: true
useKeyTab: true
storeKey: true
principal: hz/[email protected]
keyTab: hz-app1.keytab
- name: krb5Initiator
authentication:
jaas:
- class-name: com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule
usage: REQUIRED
properties:
isInitiator: true
useTicketCache: false
doNotPrompt: true
useKeyTab: true
storeKey: true
principal: hz/[email protected]
keyTab: hz-app1.keytab
member-authentication:
realm: kerberosRealm
client-authentication:
realm: kerberosRealm
client-permissions:
all:
principal: "Acme Cache"What’s new here are the explicitly defined Krb5LoginModule configurations
in security realms krb5Initiator and krb5Acceptor.
We also added the ldap sub-section in kerberos authentication. It’s responsible
for searching recursively the group names which are used as client’s roles.
The last change is defining the client-permissions section. We add one
universal permission which allows clients with role Acme Cache assigned all
operations on the cluster.
When we restart the members with this new configuration, they should again form the cluster. The console is without warnings related to the simplified Kerberos config now.
Check and Prepare Client Environment
We will run the Hazelcast Client Demo application on the application Windows Server.
Let’s make sure the active user is authenticated to the domain using Kerberos
first. Let’s use the klist tool in Windows (C:\Windows\System32\klist.exe).
C:\Users\hazelcast>C:\Windows\System32\klist.exe
Current LogonId is 0:0x1fda985
Cached Tickets: (2)
#0> Client: hazelcast @ ACME.COM
Server: krbtgt/ACME.COM @ ACME.COM
KerbTicket Encryption Type: AES-256-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96
Ticket Flags 0x40e10000 -> forwardable renewable initial pre_authent name_canonicalize
Start Time: 11/9/2020 8:44:37 (local)
End Time: 11/9/2020 18:44:37 (local)
Renew Time: 11/16/2020 8:44:37 (local)
Session Key Type: AES-256-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96
Cache Flags: 0x1 -> PRIMARY
Kdc Called: DC1.acme.com
...If the krbtgt ticket is not listed in your environment, then try to logout and newly login
with a Windows domain account.
To make sure Java can access this ticket (stored in the Windows LSA store), we need to allow access of external applications to the store. Let’s run the following command:
Reg Add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\Kerberos\Parameters /v AllowTGTSessionKey /t REG_DWORD /d 1Configure Hazelcast client
Let’s create the hazelcast-client.yml configuration file in the demo directory
within the Hazelcast installation.
hazelcast-client:
network:
cluster-members:
- 10.0.0.10
- 10.0.0.11
security:
kerberos:
security-realm: krb5Initiator
realms:
- name: krb5Initiator
authentication:
jaas:
- class-name: com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule
usage: REQUIRED
properties:
isInitiator: true
useTicketCache: true
doNotPrompt: trueThe Kerberos configuration on the client side is similar to the member configuration.
We just need to define the kerberos identity and reference its Krb5LoginModule
configuration.
We don’t define a keytab file, but we want to use existing credentials,
so we set the useTicketCache option value to true.
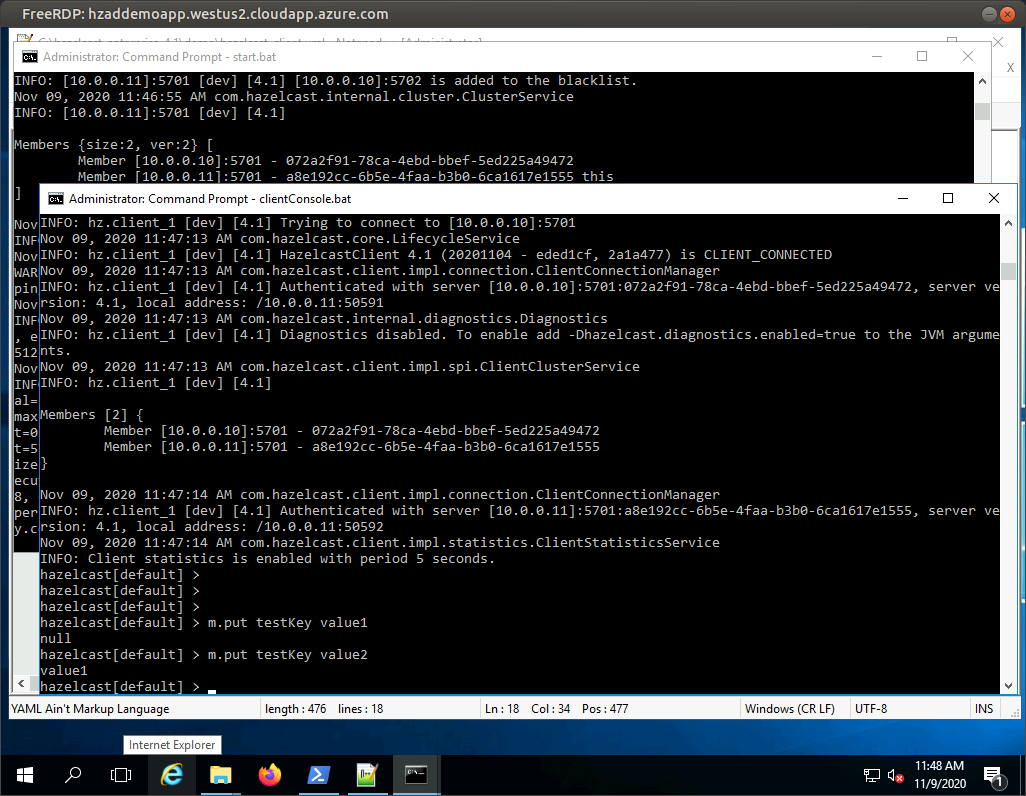
Run the client demo application
The client configuration is ready, let’s start the client application now:
cd \hazelcast-enterprise-4.1\demo
clientConsole.batThe application should successfully connect to the cluster and data operations should work.
Troubleshooting
Did anything go wrong in your setup? Try to look in more detail what’s happening underhood. Hazelcast and Java itself provide system properties which allow printing Kerberos related debug messages to console.
You can also reconfigure the log level for the com.hazelcast.security category to inspect
authentication flow within the Hazelcast login modules.
Just edit the Hazelcast batch files (start.bat, clientConsole.bat) and
add the following arguments to the java program call:
-Djava.util.logging.config.file=debug-logging.properties \
-Dsun.security.krb5.debug=true \
-Dsun.security.jgss.debug=trueCreate the new debug-logging.properties file beside the batch file:
handlers=java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler
.level=INFO
java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.level=ALL
java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter.format=%1$tF-%1$tT [%4$s] %2$s %5$s%6$s%n
com.hazelcast.security.level=ALLYou can also add the debug option to Krb5LoginModule configuration. E.g.
- name: krb5Initiator
authentication:
jaas:
- class-name: com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule
usage: REQUIRED
properties:
debug: trueSummary
We have configured the Hazelcast Enterprise cluster with Kerberos-based authentication on the Active Directory domain.
First, we used the simple Kerberos configuration just for member authentication. Then we added the full configuration and also included the client configuration. The client authorization was based on group membership defined in the Active Directory.
See Also
-
Kerberos authentication section in Hazelcast Reference manual
-
Krb5LoginModule documentation
